
Stories of chemical solvents often begin in dusty laboratories, but the journey of isopropyl acetate springs from the chemical industry's creativity and real world needs. Back in the 20th century, as paints grew more complex and industries shifted towards ever-faster drying times and better workability, chemists looked for flexible, effective esters. Isopropyl acetate showed up on their benches as a byproduct of reactions between isopropanol and acetic acid. Companies in North America and Europe popularized this compound, catching on to its value thanks to properties that put it a notch above older solvents such as ethyl acetate in some cases. Industrial firms soon started mass production, helping it move from lab curiosity to a staple in coatings, inks, and flavors.
Isopropyl acetate shows up as a clear, colorless liquid with a subtle fruity smell. Its chemical formula, C5H10O2, lands it in the family of esters – a group known for their signature scents and solvency. Chemically, it comes from blending isopropanol and acetic acid, giving it a delicate balance between volatility and solvent strength. The product gets bottled and shipped to all sorts of industries needing a solvent that can play well with many resins and oils, or to serve as a medium in analytical chemistry and flavor formulas. In my experience, noticing its smell always takes me back to work tables covered in fresh adhesives and cleaning solutions.
This compound boils near 89°C and melts at -73°C. Thanks to its vapor pressure and moderate volatility, it evaporates from surfaces fairly quickly, making it useful for quick-drying coatings. It brings a specific gravity around 0.87, lighter than water, which makes for easier handling in large batching tanks or mixing vessels. Solubility lands somewhere in the middle: it mixes with organic solvents but resists full blending with water. Flammability sits near the top concern for users, with a flash point of about 2°C, so it demands respect in hot workshops or unventilated spaces. Chemically, it's fairly stable – though acids or bases will break it down and some strong oxidizers could trigger dangerous reactions.
Each drum, can, or bottle gets marked with information that matters for safe use and compliance. Labels include molecular weight (102.13 g/mol), purity levels (often exceeding 98%), and batch traceability data. Regulatory frameworks from the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and local authorities demand hazard pictograms, precautionary phrases, and handling instructions. The UN number for shipping sits at 1220, flagged as a flammable liquid. Even before opening the seal, operators scan for signs of leakage, proper transport labeling, and storage temperatures, making sure they're not risking a mishap.
Manufacturers run a straightforward esterification, bringing together isopropanol and acetic acid in the presence of a strong acid catalyst – most often sulfuric acid. The heated reaction vessel churns out isopropyl acetate and water. Factories use distillation to separate the desired product, recirculating unreacted raw materials to minimize waste. This method offers large yields and scalable production, so supply lines keep pace with industry demands. Modern factories add in-feed controls and reaction monitoring, shrinking chances for runaway reactions or excess byproducts. I’ve seen plants pivot towards continuous processing—cutting energy use and keeping products purer than batch processes managed by less modern controls.
Isopropyl acetate’s main chemistry rests in its ester group. Under strongly acidic or basic conditions, it hydrolyzes, giving back isopropanol and acetic acid. This reaction means accidental spills in high-humidity or caustic settings can slowly degrade it, changing solvent properties on the fly. Industry chemists sometimes tweak formulation – swapping acetic acid for other acids, or isopropanol for ethanol, to craft custom esters. When clients need a different evaporation rate or scent, small structural changes yield big differences. Its chemical stability supports blending with resins, plasticizers, and other additives without premature breakdown.
Catalog listings and shipment manifests might call it 1-methylethyl acetate, acetoxypropane, or 2-propyl acetate. Trade names flip depending on supplier, sometimes showing up as IPAc or Propan-2-yl acetate. For regulatory filing, the CAS registry number 108-21-4 pins this compound for customs and compliance. Recognition in the field often comes from the scent rather than the name, at least among technicians and hands-on operators who work daily with drums and sprayers. Brand names fade, but the chemical structure stays the same.
A solvent as volatile and flammable as isopropyl acetate needs protocols. Splashes trigger skin and eye irritation. Fumes in closed spaces cause headaches or dizziness, and concentrated vapors may lead to central nervous system depression. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) detail permissible exposure limits: the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) suggests a threshold limit value of 250 ppm for an average work shift. Handling this chemical calls for goggles, gloves, and well-ventilated spaces. I once worked at a plant where routine fire drills and spill response training ensured team safety. Storage means grounded drums, temperature control, and keeping ignition sources at bay.
Paint manufacturers rely on isopropyl acetate’s fast evaporation and solvency for specialty lacquers and inks. It thins resins, dissolves cellulose derivatives, and leaves little residue, so industries from automotive to printing prefer it for uniform coatings. Flavor chemists use it at low concentrations to spark fruity notes in food and fragrance compositions. Pharmaceutical labs turn to it as a reaction medium or for extractions. In adhesives, it creates bonds that cure hard and strong without lingering stickiness or softening. Everyday encounters in consumer products – nail polish removers, cleaning sprays, and even some aerosol coatings – all hint at its versatility.
Lab research digs into finding greener processes—looking to swap out traditional acids with recyclable solid catalysts, or lower energy demands by pressure-driven esterification. Analytical teams study how small impurities shift evaporation behavior and impact sensitive resins or medical formulations. In my own practice, different grades of isopropyl acetate have been tested for chromatography, looking for the ideal solvent blend. Development never stops, with academic and corporate labs searching for esters that deliver the benefits here but with less environmental baggage or flammability. Teams tweak methods, chasing both efficiency and cleaner output.
Large scale studies on animals and humans show that acute toxicity from short-term exposure tends to be low. The LD50 (lethal dose for 50% of test rats) sits above 4 g/kg, which marks it as less dangerous compared to highly toxic solvents. Chronic studies track any long-term harm; results highlight minor liver and kidney effects at massive exposures—far above usual workplace routines. Irritation comes up more often in field reports, usually with poor ventilation or careless handling. Workers who inhale high concentrations for long periods report headaches or tiredness, pointing to the need for proper engineering controls, training, and medical monitoring in busy sites.
As industries keep demanding safer solvents and lower emissions, producers look at how to minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal. Bio-based alternatives creep into the discussion, hinting at renewable isopropanol or acetic acid feedstocks. Cleaner process tech targets less energy use and more recycling of spent solvent. Regulations likely will keep tightening, nudging companies to adopt best practices sooner. New uses in electronics, specialty coatings, and even biotech promise fresh markets, but bring with them a call for ever-stricter purity and handling standards. Isopropyl acetate maintains its place as an industry favorite, balanced between tradition and constant reinvention.
Once you get past the tongue-twister name, isopropyl acetate shows up as a clear, sweet-smelling liquid you’ll find tucked away on the labels of nail polish removers, printing inks, and some cleaning products. Its scent gives away its alcohol family roots, but it’s the blend of evaporation speed and solvency that sets it apart in the chemical world. Unlike alcohol itself, it packs a bit more punch when it comes to tackling grease and dissolving tough residues.
Take a look under your bathroom sink. Any product that promises to wipe away layers of polish or heavy adhesives likely leans on isopropyl acetate. Nail salons depend on it for fast, streak-free removal, and the same goes for folks who do their own manicures at home. Its solvent power cuts through even the most stubborn lacquers. I have seen my own coffee table rescued from sticker residue thanks to a quick dab of nail polish remover containing it.
Printers and press operators count on isopropyl acetate to get crisp, clean results. Ink formulations use it because it dries quickly, which helps speed up production lines. It’s found in printing plants that want to avoid blotchy results on glossy magazines or packaging. While helping inks dry fast, it also doesn’t leave behind much residue, which means less fuss during cleanup.
Isopropyl acetate plays a quiet but important role in electronics and precision cleaning. It removes organic grime from delicate parts, like circuit boards, without causing damage—something every technician appreciates. Speed counts in electronics repair, and this solvent gets the job done before parts begin to corrode. Not all solvents strike that balance between tough cleaning ability and safe evaporation, and I’ve watched more than one friend breathe a sigh of relief as it lifted marker from a phone’s screen without a trace.
Calling it safe wouldn’t do the whole story justice. Isopropyl acetate carries flammability risks, and its fumes irritate airways if there’s not enough ventilation. Health agencies have flagged these hazards for workplaces, and safety data sheets spell out everything from splash prevention to fire safety. Around the home, most folks don’t realize that extra ventilation and a pair of gloves can keep small-scale projects from turning into headaches.
The EPA and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health both lay out standards for handling and air exposure. Regular industrial audits and training shake people out of routine, reminding workers to limit inhalation and keep the solvent away from open flames. These guidelines aren’t just a formality—they’re built around years of occupational studies and emergency reports.
Green chemistry groups and some manufacturers have started searching for alternatives that aren’t as volatile. Though it’s tough to beat isopropyl acetate’s speed and strength, research into bio-based solvents offers new hope. Consumers looking for low-impact options can make a difference by reading labels and supporting companies that take chemical safety seriously.
In my own toolbox, I still reach for isopropyl acetate for jobs where nothing else comes close. Its utility can’t be ignored, but a healthy respect for glove use and open windows keeps my DIY jobs both safer and more effective.
Isopropyl acetate pops up in many places, but most folks barely notice it. The fruity smell sometimes signals its presence in printing shops, paint factories, or even in household products. Understanding what happens when people come into contact with this chemical makes a difference, especially in environments where spills or fumes are likely.
Short-term exposure to isopropyl acetate usually causes irritation. Breathing in the vapors can lead to headaches, dizziness, or even nausea. I’ve walked through a shop floor after someone knocked over a jug of a similar solvent, and the overpowering smell drove most people out in seconds. For folks working daily around these types of chemicals, strong ventilation becomes a non-negotiable issue. Touching the liquid stings the skin and can dry it out, and it irritates the eyes. The risk grows with larger spills or poor ventilation. Chronic exposure multiplies these issues, running a real risk of damaging the respiratory tract or affecting the central nervous system.
According to data from agencies like the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), isopropyl acetate carries a recommended exposure limit on the order of 250 ppm over an eight-hour shift. Owners and safety managers have a job to keep those numbers in mind and check for proper handling and storage. It doesn’t rank as one of the most toxic chemicals out there, but the risks are real—and they add up when precautions slip or maintenance lags.
This chemical evaporates quickly, and the vapors can catch fire with just a spark or static jolt. I’ve seen a misguided shortcut or two—leaving rags or open containers in the sun—nearly end in disaster. Isopropyl acetate doesn’t care about your schedule or deadlines; it reacts fast and burns hotter than most folks expect. Fire safety plans must fit this risk, and workers must avoid using open flames or even switching on electric tools nearby unless conditions stay controlled.
Spilled isopropyl acetate evaporates before it soaks deep into the ground, but in big enough quantities, vapor forms can hang around and drift into nearby offices or homes. Waterways could carry it farther, where it changes the flavor of drinking water and disrupts aquatic life. Some communities near manufacturing hubs have faced real annoyances and health complaints tied back to leaks. Keeping tight controls and fast clean-up make a difference not just for workers, but for neighbors too.
Good training and reliable equipment form the backbone of safety. Workers have to get past the urge to “just finish the job” without eye protection, gloves, or enough airflow. Locking up containers and labeling them makes sure no one else gets a nasty surprise. Spills need immediate cleanup—cat litter or special chemical-absorbent pads work much better than a pile of old towels. Regular air quality checks help, too; handheld meters show workers if levels creep up. Even busy crews have found that slowing down for five extra minutes saves plenty of trouble down the line.
In my experience, management walks the walk when they deliver short refresher lessons every few months. Inviting suggestions from crew members—the ones who handle chemicals day in and day out—brings fresh ideas and heads off blind spots. Keeping isopropyl acetate out of the headlines starts with looking after the people who work with it every day and building a workplace where safety sticks.
Isopropyl acetate stands out thanks to its crisp, fruity odor and clear, colorless appearance. Dozens of plants smell the same sharp, sweet note because of solvents like this. Anyone who’s opened a can of nail polish remover or lacquer thinners has probably breathed it in, even if just for a moment. The molecule picks up attention for its balance of volatility and solvency—the two features that make it useful and a little risky if mishandled.
Pour isopropyl acetate out in a lab or a factory and it doesn’t stick around. It evaporates quickly, boiling at about 89°C (192°F). That low boiling point minimizes drying time whenever the solvent gets used in coatings or inks. Even in cold rooms, you don’t have to wait long before it vanishes off a solid surface. Quick evaporation means faster processing in industrial jobs, but it also fuels fire risks in closed spaces.
Weighing less than water—clocking in near 0.87 grams per cubic centimeter—isopropyl acetate floats if poured into a beaker of water. That difference in density makes separating spills in mixed environments less messy than with heavier solvents. It likes to blend with many organic liquids such as alcohols, ethers, and other esters. Splash it into plain water, though, and it only dissolves sparingly. That puts a limit on how much can end up in groundwater or wastewater streams, another thing regulators and chemists keep an eye on.
It’s easy to get distracted by the convenience of a fast-evaporating solvent, but isopropyl acetate lights up at 2°C (35°F) and has a flash point around 2°C (35°F) in closed-cup tests. That’s colder than many household freezers. The risk this brings to warehouses, printer shops, and beauty salons can’t be ignored. One careless spark can turn this common liquid into an emergency. Understanding that danger shapes the way good operators handle storage, ventilation, and waste.
People who work with this solvent know that its irritant properties show up fast—eye and skin contact often means discomfort. Inhalation exposures are more likely as the liquid turns into vapor quickly. Health regulations call for limiting airborne concentrations in workspaces; this prompts efforts to boost containment, use fume hoods, and rotate staff. Keeping containers closed tight and storing them in fire-safe cabinets is second nature in responsible labs and shops.
Isopropyl acetate appears in products like coatings, cleaning agents, and perfumes for many reasons: its physical profile makes tasks quicker and dissolution more thorough with less residue left behind. The trick is to harness these properties while cutting down risks. Safer labeling, improved training, and rethinking the workplace design all help lower the chance of smoky surprises or accidental injuries.
Chemistry isn’t always just numbers in a table. The way isopropyl acetate behaves—its smell, how fast it goes from liquid to vapor, the danger in a capped jar—affects daily routines in science labs and workshops alike. Simple steps like proper labeling, regular training, and fire prevention keep its useful side front and center without letting the hazards take over.
Isopropyl acetate turns up on safety data sheets across labs, paint shops, and factories. It brings a fruity smell, wins people over in perfumery, and shows up in coatings and solvents. That same pleasant scent signals a warning. Underestimating it has sent emergency crews scrambling. Personal experience in research labs has shown even seasoned workers can get careless with this liquid.
Once isopropyl acetate hits the air, it vaporizes quickly. Vapors build up, float near the floor and can catch fire fast. Even a small spark from a static charge or faulty outlet could start a blaze. Inhaling those vapors flips switches in the nervous system—headaches come quick, and coordination drops off fast.
Long before modern safety policies, smaller shops and labs sometimes stashed bottles just about anywhere. Broken bottles and faint solvent clouds told their own story. These mishaps didn’t need to happen. With better information and stricter standards, the risks drop dramatically.
Keeping isopropyl acetate in the right space makes all the difference. Store it in a cool, well-ventilated room. Skip any spot near heaters, open flames, and sunlight. Secure metal cabinets with proper ventilation offer solid protection. Explosion-proof refrigerators exist for a reason. They keep vapors from finding their way to motors and switches.
Containers hold a lot of responsibility. I’ve seen old labs with crusty metal drums leaking at the seam and cheap plastic bottles warped from contact. Go for high-quality, airtight containers built for flammable chemicals. Seal them after every use, and never let the rim get sticky—cleanliness is part of the safety equation.
Anyone handling isopropyl acetate earns a set of gloves, splash goggles, and a chemical apron. I still remember a colleague learning this lesson after wiping solvent off a bench without gloves—irritation set in fast. Don’t breathe in the vapor—if a whiff hits you, step out, and check ventilation. Only handle it where a working fume hood or powerful exhaust system clears fumes quickly.
In the middle of a spill, people freeze. Knowing where spill kits and absorbent pads live beats panic. Cleaning up means working from the outside in, then disposing of everything as hazardous waste. Dumping leftovers down the drain or trash risks spreading fumes or fire.
Training stays vital. Review safety guidelines often. Practice spill drills in small teams. Label storage areas with big signs for everyone to see—don’t hide the hazard away. Keep fire extinguishers that handle flammable liquids close. Each small step chips away at the possible mistakes. The right gear, good habits, and clear rules keep work moving without close calls. Past slip-ups taught me the true cost of ignoring precautions. Storage and handling practices shape outcomes—avoiding shortcuts keeps everyone safer.
People cross paths with isopropyl acetate more often than they think. This solvent shows up in nail polish removers, printing inks, and coatings. Its strong smell gives it away, but the real risks come from its flammable nature and its impact on skin and lungs. Many people have seen workplace labels and SDS sheets, but habits keep safety at arm’s length—until something goes wrong.
Isopropyl acetate evaporates fast and catches fire easily. Just a small spark or static charge near a leaking bottle can trigger a disaster. I remember once watching a rush job in a print shop—someone forgot to close a can, fumes spread, and nearby electronics nearly turned a mistake into an emergency. Fires like these move fast, so storing this solvent away from heat and static sparks makes a difference. Grounding metal containers helps kill the static threat.
Keeping rooms airy matters. Good air flow carries away fumes before they gather on the floor, since these vapors are heavier than air. It’s easy to ignore hissing sounds or lingering smells, but reporting small leaks instead of plugging them with random rags stops a lot of trouble from growing bigger.
Many skip gloves, but I’ve seen how isopropyl acetate pulls oils straight out of skin. After a long shift, I once got a painful rash between my fingers—there’s a reason gloves made of nitrile or neoprene matter. Safety glasses help dodge splashes in the eye. Workers can recognize the sharp sting and blurry vision that comes from a tiny drop, and even a quick rinse at the eyewash station burns when the solvent’s involved.
Breathing matters, too. Most folks brush off a little headache as just part of the job, not tracing it back to solvent vapor. A certified organic vapor mask or a proper respirator in tight indoor space means breathing is never a gamble. I’ve seen old-timers block vents with cardboard to keep warm, only to complain about dizziness an hour later. No one should have to choose warmth over clean air.
Spills happen, and hesitation makes them worse. Keeping spill kits close, with absorbent pads and disposal bags, helps keep panic out of the picture. Once, I witnessed a colleague toss sand instead of the right absorbent, turning a small puddle into a gluey mess that spread further. Training sessions that mimic real spills stick in memory more than any memo or email.
Disposal can’t become an afterthought. Rinsing left-over solvent down the drain creates bigger headaches—both for the environment and anyone downstream. Sealed waste cans with clear labels help remind people that what’s in there won’t just vanish.
One person being careful isn’t enough. Real safety means everyone from new hires to seasoned veterans calls out unsafe habits and follows the same routines. Regular talks based on quick, real-world examples replace long-winded safety lectures with something people remember. When I worked with teams who practiced drills and quizzed each other, accident rates went down—and so did stress about "what if" scenarios.
Isopropyl acetate isn’t rare, and its dangers crop up in places as ordinary as salons and classrooms. Protecting hands, lungs, and eyes becomes less about strict rules and more about keeping workdays as safe as possible. Small habits—closing lids, cleaning up right away, keeping the air moving—stack up to make a real difference.
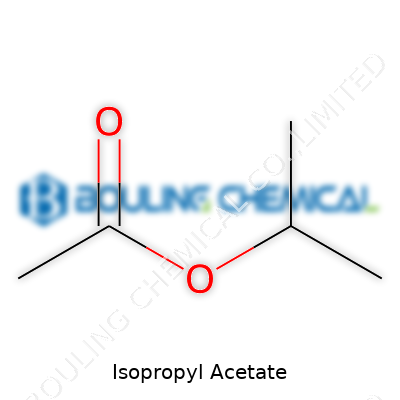
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | propan-2-yl ethanoate |
| Other names |
IPA
Isopropyl ethanoate Acetic acid, isopropyl ester 2-Propanol acetate |
| Pronunciation | /ˌaɪsəˈproʊpɪl ˈæsɪteɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 108-21-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 754478 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:37786 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL135120 |
| ChemSpider | 8808 |
| DrugBank | DB03134 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03af6eaf-ea48-4a1d-a3fe-7d8143eb6b8a |
| EC Number | 203-561-1 |
| Gmelin Reference | 8815 |
| KEGG | C01217 |
| MeSH | D017370 |
| PubChem CID | 7906 |
| RTECS number | NS8050000 |
| UNII | OX8I2XEWG5 |
| UN number | UN1220 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID0024262 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H10O2 |
| Molar mass | 102.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid with a pleasant, fruity odor |
| Odor | pleasant, fruity |
| Density | 0.87 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | 8.7 g/100 mL (25 °C) |
| log P | 1.32 |
| Vapor pressure | 33 mmHg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ 25 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb ≈ 15 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -54.2×10⁻⁶ |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.372 |
| Viscosity | 0.55 mPa·s |
| Dipole moment | 2.88 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 282.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -464.1 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3166.7 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-3-1 |
| Flash point | 2°C (36°F) |
| Autoignition temperature | 457 °C |
| Explosive limits | 1.1–7.1% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat 6,750 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | 6.75 g/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | NIOSH: NK3225000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 250 ppm |
| REL (Recommended) | 250 ppm |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 1500 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Acetic acid
Isopropanol Ethyl acetate Propyl acetate Methyl acetate |